The Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the part of the nervous system whose functions remain largely unconscious. This refers to the part of the nervous system that controls the functions of internal organs. These are autonomous, that means independent of willful influence. That's why the British physiologist John Newport Langley (1852-1925) coined the term autonomous nervous system.
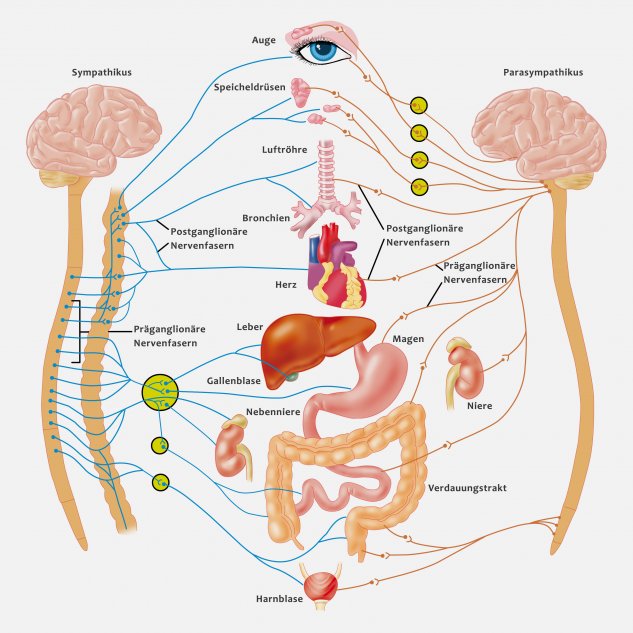
The autonomic nervous system connects the central nervous system with almost all body organs and thus controls basic life functions such as blood circulation, digestion, respiration or temperature regulation. While the brainstem controls important reflexes such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system controls the functions of the internal organs. These include the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, saliva production, sweating, pupil width, bladder emptying etc. The interactions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves are well coordinated. While the impulses of the sympathetic usually have a rapid and mobilizing effect, parasympathetic impulses have more damaging effects on many organs.

„You have questions about ANS Clinic or would like to make an appointment? I'm happy to help.“
Prof. Dr. Med. Christina Haubrich